SNMP
Configuration
i You will find the SNMP configuration in the web interface under Configuration - General.
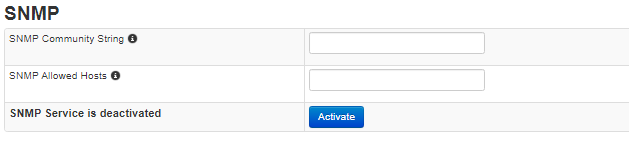
You can activate the SNMP service and set the SNMP Community String.
The SNMP Community String only supports characters, numbers and minus ( a-z A-Z 0-9 - ).
With the SNMP Whitelist you can permit the access to the SNMP Service for IPs or subnets.
Default settings
The default SNMP Community String is public and the SNMP service is deactivated.
The SNMP Whitelist is empty on default, means all (0.0.0.0/0) IPs or subnets have access.
SNMP Manager
To access the brevis.one SMS Gateway OIDs you need to download and install the MIB for the brevis.one SMS Gateway.
You can download the brevis.one SMS Gateway MIB here.
Additional callable OIDs
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.1
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.2
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.3
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.3.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.4.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.6.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.11.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.13.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.14.0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.15.0
.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0
.1.3.6.1.2.1.4.35.1.4.2.1.4
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5
.1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.1.0
.1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.10
.1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.10
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.14
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.20
From Version 24.00:
Configuration
i You can find the SNMP configuration in the web interface under Configuration - General.
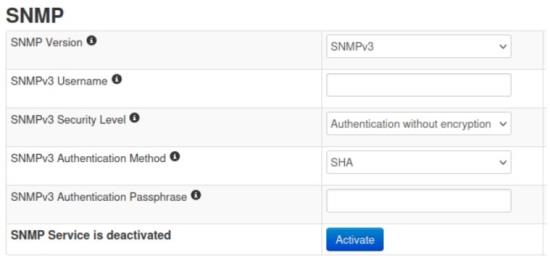
Here you can activate / deactivate the SNMP service and configure authorization options.
For SNMP Version 2
For the “SNMP Version” option choose “SNMPv2”. Then you can configure a community string.
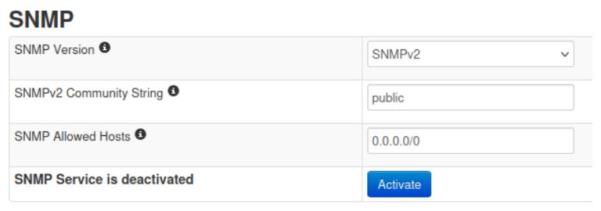
The SNMP community string may only consist of letters, digits and dashes ( a-z A-Z 0-9 - ).
The SNMP whitelist (SNMP Allowed Hosts) can restrict which host or subnet may access the SNMP service on this device.
For SNMP Version 3
For the “SNMP Version” option choose “SNMPv3”.
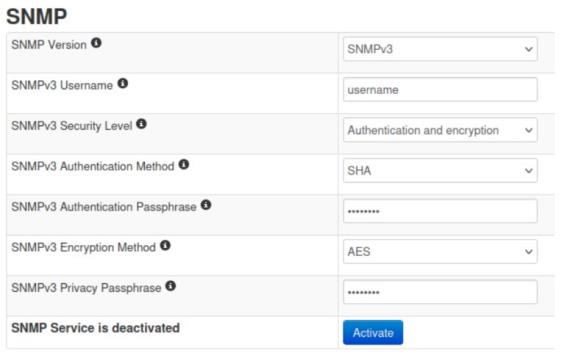
Now you can configure a user name for the SNMP user that is to be given access to the SNMP service.
In the “SNMP Security Level” field, you can now specify whether this user requires an authentication password and / or an encryption password and which authentication or encryption method should be used.
The corresponding passwords must be between 8 and 32 characters long and must not contain spaces or '?'.
Default settings
By default, “SNMP version 3” with security level *Authentication without encryption* is set and the SNMP service is disabled. To enable access to the SNMP service, a user name and, depending on the configuration, corresponding passwords must be configured.
SNMP Manager
To access the brevis.one SMS Gateway OIDs, you need the MIB for the brevis.one SMS Gateway.
You can download the brevis.one SMS Gateway MIB here: https://download.brevis.one/snmp/braintower-sms-gateway.mib
Additionally available OIDs
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.1 — Load average during first minute
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.2 — Load average during first five minutes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.3 — Load average during first fifteen minutes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.3.0 — The total amount of swap space configured for this host, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.4.0 — The amount of swap space currently unused or available, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5.0 — The total amount of real/physical memory installed on this host, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.6.0 — The amount of real/physical memory currently unused or available, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.11.0 — The total amount of memory free or available for use on this host, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.13.0 — The total amount of real or virtual memory currently allocated for use as shared memory, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.14.0 — The total amount of real or virtual memory currently allocated for use as memory buffers, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.15.0 — The total amount of real or virtual memory currently allocated for use as cached memory, in Kilobytes
.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 — The time (in hundredths of a second) since the network management portion of the system as last re-initialized
.1.3.6.1.2.1.4.35.1.4.2.1.4 — The media-dependent 'physical' address
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10 — The total number of octets received on the interface, including framing characters
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16 — The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing characters
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5 — An estimate of the interface's current bandwidth in bits per second
.1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.1.0 — The amount of time since this host was last initialized
.1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.10 — The size of the storage represented by this entry, in units of hrStorageAllocationUnits
.1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.10 — The amount of the storage represented by this entry that is allocated, in units of hrStorageAllocationUnits
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.14 — For packet-oriented interfaces, the number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. For character- oriented or fixed-length interfaces, the number of inbound transmission units that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol
.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.20 — For packet-oriented interfaces, the number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors. For character-oriented or fixed-length interfaces, the number of outbound transmission units that could not be transmitted because of errors
Best Practices
-
Prefer SNMPv3 with authentication and encryption.
-
Set strong passwords (random, min. 12 characters).
-
Restrict access to required IPs/subnets using a whitelist.
-
Test SNMP access with your SNMP manager after every configuration change.
-
Document users, passwords (encrypted), and OID usage internally.